Description
This plugin adds all the tags in the head section of a website to WordPress REST API responses.
It is perfect if you are using WordPress for a headless set-up and would like to add the meta tags generated by your WordPress SEO plugin (like Yoast SEO or All-in-One SEO Pack) to the WordPress REST API output.
Requirements
This package depends on the PHP DOM library. Most PHP environments have it by default so you don’t have to worry about that.
In case you get some errors regarding this dependency make sure you have this library installed (you can take a look at this thread in the code repository).
Compatibility
This plugin is compatible and works out of the box with some of the most popular WordPress SEO plugins. These are the ones that we tested:
- Yoast SEO – (up to 13.5)
- All in One SEO Pack – (up to 3.4.2)
- WP SEO –
Are you using a different SEO plugin and want to know if it’s compatible? Feel free to ask in our community forum. If you tested any other plugin, please let us know as well so we can update the list.
How to use this plugin
Entities with head tags
The plugin has been developed to include the head_tags field to the REST API response of most of the WordPress core entities:
- Posts, pages, attachments and custom post types.
- Post types: for archive pages.
- Categories, tags and custom taxonomies.
- Authors.
In a Frontity project
If you are using Frontity, you just have to install the @frontity/head-tags package and it will work automatically.
?In a different project
You need to understand better how it works and add the data manually.
How to fetch the head_tags field manually
You have to get each entity from its respective REST API endpoint. For example: for fetching the posts, you should go to /wp-json/wp/v2/posts&id=123 endpoint; for fetching the categories, you have to go to wp-json/wp/v2/categories&id=123, and for custom post types or custom taxonomies, it would be a different url in each case.
In the case of the homepage, it’s less intuitive and you should go to /wp-json/wp/v2/types/post. As previously said, each entity has a different endpoint so if you aren’t familiar with this, you should check out the WordPress REST API reference for more information.
Inside each endpoint, it will be a new field named head_tags, which will be an array of objects representing the tags that WordPress would normally include inside the html head element. These objects have the properties tag, attributes and content.
For example for these HTML tags:
<title>Hello wordl! - My Site</title>
<meta name="robots" content="max-snippet:-1, max-image-preview:large, max-video-preview:-1">
<link rel="canonical" href="<https://test.frontity.org/>" />
This would be the content of the head_tags field:
"head_tags": [
{
"tag": "title",
"content": "Hello world! - My Site"
},
{
"tag": "meta",
"attributes": {
"name": "robots",
"content": "max-snippet:-1, max-image-preview:large, max-video-preview:-1"
}
},
{
"tag": "link",
"attributes": {
"rel": "canonical",
"href": "<https://test.frontity.org/>"
}
}
]
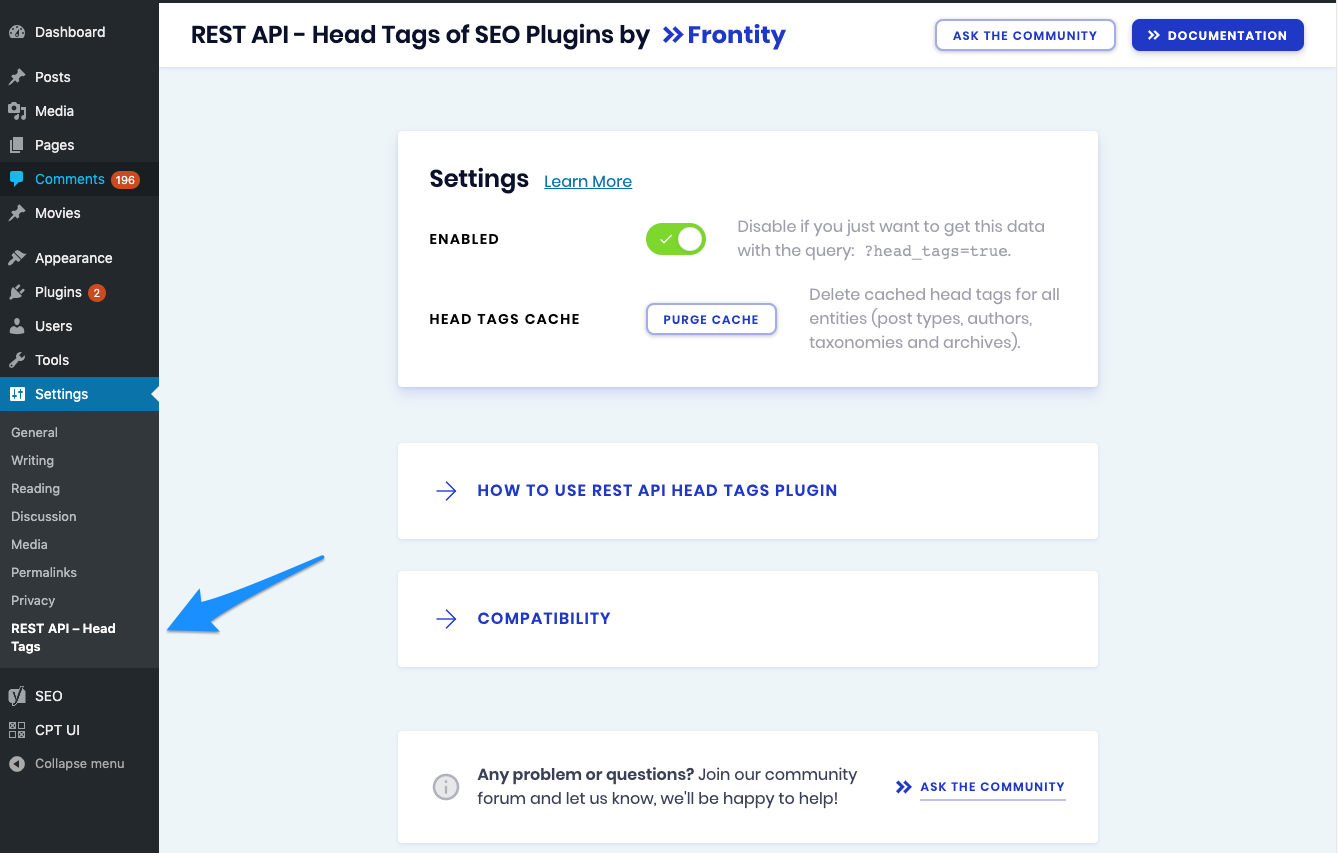
Settings
The settings of this plugin are really simple.
Purge cache
In order to not affect the performance of your site, the head_tags field is cached for all your responses. Each time you update a post/page/cpt or a taxonomy, the cache for that entity will be purged automatically. In case you make global changes (i.e. your permalinks or your global Yoast settings) use the Purge button to clean the whole cache.
?Enable output
By default, the head_tags field is included in the common endpoint of each entity. You can configure it so it doesn’t appear by default and to be shown when you include the head_tags=true query.
For example, with the output disabled, https://test.frontity.org/wp-json/wp/v2/posts won’t show the head_tags field unless you have the query ?head_tags=true at the end.
Skip cache
In case you want to skip the cache, you can do so by adding to the query the parameter skip_cache.
There are some cache plugins for the REST API which also use the same parameter. In case you want to ignore the cache for the REST API call but not for the head tags, you can use skip_cache&head_tags_skip_cache=false.
Problems and Questions
If you have any trouble with the REST API – Head Tags, you can check out our docs or join our community forum and let us know. We’ll be happy to help!
Bug reports for REST API – Head Tags plugin are welcomed in our repository on GitHub. Before opening an issue, please be sure to review the contributing guidelines.
More Information
- About Frontity Framework
- Guide on SEO for Headless WordPress Themes
- Follow Frontity on Twitter and GitHub
- Get help on the Frontity Community Forum
Installation
-
First of all you have to install the plugin. You can do it:
- Automatic: from within WordPress dashboard go to Plugins, click Add New button, search for REST API – Head Tags by Frontity and click Install Now.
- Manual: this method requires to download the plugin and upload it to your web server via FTP. For a more detailed explanation, WordPress explains how to do this on this guide.
-
Once installed, you have to activate it and it will be running! The head_tags field is cached and enabled by default, but you can purge the cache or disable the output as explained on the Settings section.
FAQ
-
Can I use the plugin only within a Frontity project?
-
No, you can use it for any headless WordPress project. However, if you use Frontity, you can get all the data automatically with this Frontity package. On the other hand, if you are not using Frontity, you have to add the data manually as explained on the plugin’s documentation.
-
You can find the head tags exposed in the WordPress REST API after making an API request. You can find a new field named
head_tagswhich is an array of all the meta tags, just as they appear in the web page section. You can see more information at the plugin docs. -
If you are not using this Frontity package (which will automatically add the head tags), you should fetch this data at
/wp-json/wp/v2/types/postendpoint. -
Yes, the plugin will automatically add the meta tags to the custom post types and custom taxonomies. You can check which entities show the new field on its docs.
-
Is this plugin compatible with Yoast SEO plugin? And with All in One SEO Pack?
-
Yes, it works with both Yoast SEO and All in One SEO plugins. We actually plan to make it compatible with most of the WordPress SEO plugins. If you test it with any other plugin, kindly let us know whether it works or not so we can update the list.
Reviews
Contributors & Developers
“REST API – Head Tags” is open source software. The following people have contributed to this plugin.
ContributorsTranslate “REST API – Head Tags” into your language.
Interested in development?
Browse the code, check out the SVN repository, or subscribe to the development log by RSS.
Changelog
1.2.1
Patch Changes:
– Return an empty array when there is no <head> tag.
1.2.0
Minor Changes:
– Add support for the latest version of the All In One SEO plugin (^4.0.16).
1.1.4
Patch Changes:
– Remove warning messages from REST API responses when head’s HTML code is malformed.
1.1.3
Patch Changes:
– Fix redirects to images when making calls to the REST API in a site with Yoast installed.
– Also, refactor the code to prevent other redirections in the future.
1.1.2
Patch Changes:
– Fix the performance of the clear cache functionality.
– Fix the way admin hooks and rest api hooks are being registered.
1.1.1
Patch Changes: Fix redirects when making calls to the REST API.
1.1.0
Minor Changes: Added integration with All In One SEO Pack plugin.
1.0.1
Patch Changes: Fix the registering of activation / deactivation hooks.
1.0.0
Major Changes: Release the first version of REST API – Head Tags plugin.